PLANTAR FASIOPATHY
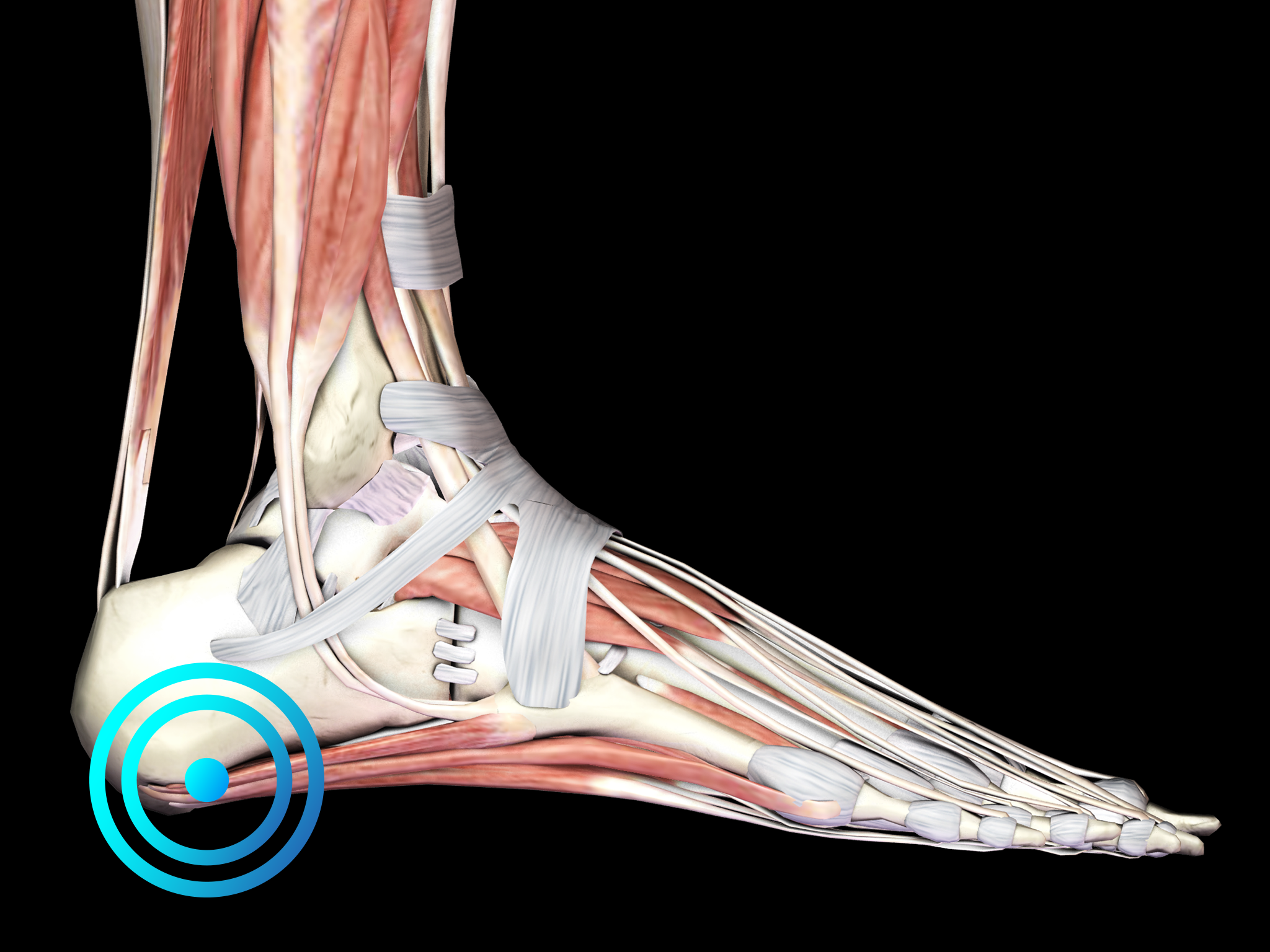
Plantar fasciopathy (PF) is an acute or chronic, painful disorder of the plantar fascia that spans between the medial calcaneal tubercle and the proximal phalanges of the toes.
Pathology
It is the most common cause of plantar heel pain and accounts for approximately 11-15% of foot symptoms presenting to physicians. The main clinical symptom is heel pain, particularly in the morning or after a period of rest. Often patients report improvement of pain after walking. Pain is usually located at the origin of the plantar fascia, i.e., at the medial calcaneal tubercle. Passive dorsiflexion of the toes may aggravate the pain in some patients, particularly in those with chronic PF. Patients suffering from chronic PF may also present with heel pad swelling.
Diagnosis is based on the clinical features of the disease. Diagnostic imaging should be considered to rule out other causes of plantar heel pain or to establish the diagnosis of PF when in doubt. Histologic examination of biopsy specimens from patients undergoing plantar fascia release surgery for chronic symptoms has shown that chronic PF is associated with degenerative changes in the fascia.
Accordingly, the disease is better characterized as “plantar fasciopathy” than “plantar fasciitis”, resembling the situation in overuse tendon problems.
In the United States, more than two million individuals are treated for PF on an annual basis. Up to 10% of the population will experience plantar heel pain during the course of a lifetime.
Both athletes and the elderly commonly present to physicians with PF. The treatment of PF should start with conservative treatment modalities including rest, physiotherapy, stretching, exercises, shoe inserts/orthotics, night splints, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and local corticosteroid injections.
Patients not responding to conservative treatment for six months (between 10% and 20% of all patients) shall then undergo radial shock wave therapy for plantar fasciopathy.
Surgery should be considered for recalcitrant cases of PF.
Side effects of Radial Shock Wave Therapy (RSWT®) using the Swiss DolorClast®
When performed properly, RSWT® with the Swiss DolorClast® has only minimal risks. Typical device-related non-serious adverse events are:
- Pain and discomfort during and after treatment (anesthesia is not necessary)
- Reddening of the skin
- Petechia
- Swelling and numbness of the skin over the treatment area
- These device-related non-serious adverse events usually disappear within 36h after the treatment.
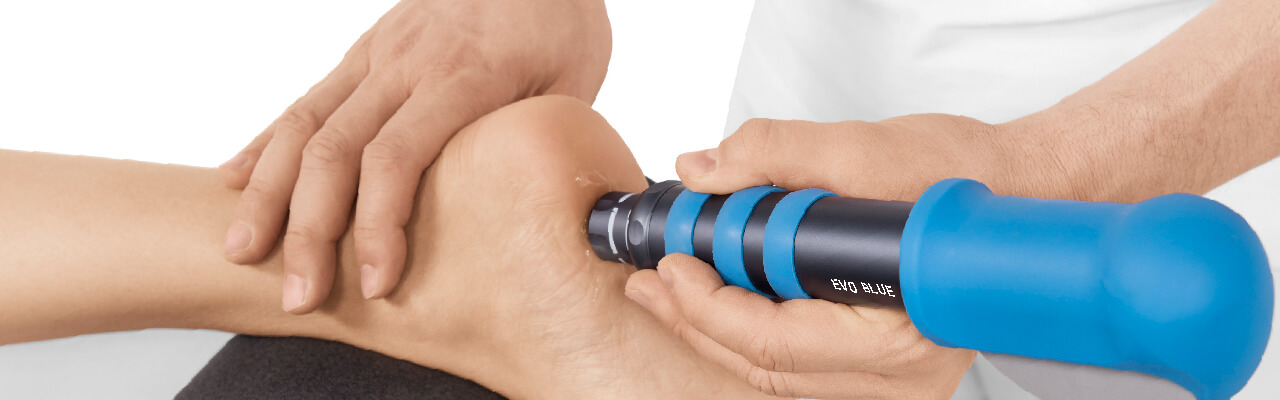
Treatment Procedure

Palpate
Locate the area of pain through palpation and biofeedback.

Mark
Mark the area of pain.

Apply gel
Apply coupling gel to transmit shock waves to the tissue.

Apply shock waves
Deliver Radial or Focused Shock Waves to the area of pain while keeping the applicator firmly in place on the skin.
Clinical Proof
Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is safe and effective in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant plantar fasciitis: results of a confirmatory randomized placebo-controlled multi-center study.
Gerdesmeyer L, Frey C, Vester J, et al.
Am J Sports Med 2008;36:2100-2109
Chronic plantar fasciopathy can be treated efficiently with radial shock wave therapy, which can be administered to outpatients without having to reccur to anesthesia. This randomized controlled trial aims at demonstrating therapeutic superiority vs. placebo.
View Study →
Successful treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis with two sessions of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy.
Ibrahim M, Donatelli R, Schmitz C, et al.
Foot & Ankle Int. 2010 May; 31 (5):391-97 20460065
Radial shock wave therapy has been demonstrated to be an effective method to treat chronic plantar fasciopathy in three sessions. This study aims at showing that two sessions are already sufficient to treat this pathology with ESWT.
Recommended Settings
| Recommended Settings | Treatment | Myofascial Therapy |
| Number of treatment sessions | 3 to 5 | 3 to 5 |
| Interval between two sessions | 1 week | 1 week |
| Air pressure Evo Blue® | 2 to 4 bar | 3 to 4 bar |
| Air pressure Power+ | 1.5 to 3 bar | 2 to 4 bar |
| Impulses | 2000 on the painful spot |
2000
|
| Frequency | 8Hz to 12Hz | 12Hz to 20Hz |
| Applicator | 15mm | 36mm |
| Skin pressure | Moderate 3 sides of the tendon | Moderate to Heavy |
Contraindications
The following contraindications of RSWT using the Swiss DolorClast® must be considered:
- Treatment over air-filled tissue (lung, gut)
- Treatment of pre-ruptured tendons
- Treatment of pregnant women
- Treatment of patients under the age of 18 years (except for Osgood-Schlatter disease and muscular dysfunction in children with spastic movement disorders)
- Treatment of patients with blood-clotting disorders (including local thrombosis)
- Treatment of patients treated with oral anticoagulants
- Treatment of tissue with local tumors or local bacterial and/or viral infections
- Treatment of patients treated with cortisone
Some indications may not be approved in the United States of America, under regulation by the US FDA. Please refer to the respective Instructions for Use.
